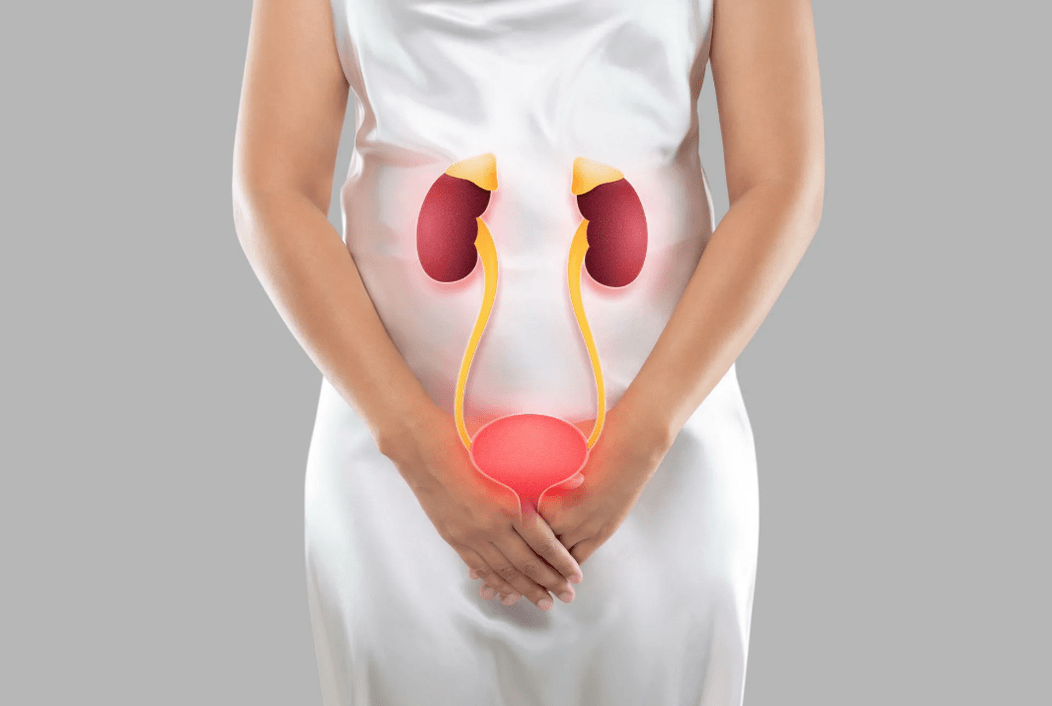
Cystitis is one of the most frequently diagnosed diseases in the field of urology. This is the number 1 urological disease that almost every woman faces at least once in her life. It is an inflammatory pathology of the urinary bladder, which occurs due to the penetration of pathogenic microflora into the bladder. As a result, bacteria multiply inside the bladder, leading to a series of characteristic symptoms. In rare cases, the disease occurs due to allergic or toxic effects.
Important!
The information in this article should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. You should always consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Most often, cystitis occurs in women, which is related to the structural characteristics of the urinary system. According to statistics, more than 30 million cases of this disease are detected annually in our country. Moreover, more than half of annual visits to the urologist are related to inflammation of the bladder in an acute or chronic form.
Treatment of cystitis is aimed at eliminating existing symptoms and normalizing the work of the entire genitourinary system. In the article, we will talk about the main causes of pathology, signs of its development, features of therapy and prevention.
Types of cystitis
Depending on the characteristics of development and flow, several types of the disease are distinguished. According to the pathogenesis (i. e. the mechanism of development), the following types of cystitis are distinguished:
- Primary (uncomplicated). It occurs as a separate independent pathology, as a rule, it occurs in relatively healthy patients who do not have urinary outflow disorders.
- Secondary (complicated). It can be a consequence of a violation of the outflow of urine in a number of concomitant diseases: for example, urolithiasis or tumor formation in the pelvic organs.
Depending on the etiology (causes of development), the following types of cystitis can be distinguished:
- Contagious. It becomes the result of the action of bacteria on the tissues of the organs.
- Toxic. It occurs as a result of the harmful effects of toxins, drugs, as well as due to radiation or chemotherapy.
- Allergic. It becomes a consequence of exposure to various allergens.
A separate classification of the disease is carried out taking into account morphological changes:
- catarrhal cystitis. It is characterized by damage to the upper layers of the bladder mucosa. In addition, swelling and hyperemia (state of increased blood flow to organs) occur.
- Hemorrhagic. It leads to inflammation of the blood vessels, which causes blood to seep into the urine.
- Ulcerative fibrous. It is characterized by the spread of the inflammatory process to the muscle tissue of the organ.
- Gangrene. Associated with the development of necrotic changes on the walls of the bladder.
- Intermediate. The inflammatory process extends to the organ mucosa, submucosa and muscle layer.
A separate form of cystitis is often called the postcoital variant ("honeymoon cystitis"). This variant of the disease occurs after defloration. This is due to the penetration of vaginal mucus into the urethra.
Also, according to the stages of the course, acute and chronic (recurrent) cystitis are distinguished. The acute form is characterized by an uncomplicated course and has clear symptoms. If the disease has become chronic, then the characteristic symptoms of the patient appear only in periods of deterioration.
Important!
The information in this article should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. You should always consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of the disease
Signs of cystitis can be very diverse and often depend on the form of the pathology. If we talk about the general symptomatic picture, then the following is most common:
- Frequent urge to urinate (the normal number of urinations during the day is about 6-10 times).
- Discomfort in the bladder area, feeling of fullness.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Burning and cutting during urination.
- Change in urine color, presence of impurities (blood or mucus).
There are also general symptoms of intoxication. A woman may feel chills, weakness, fatigue, fever, heavy sweating. In more severe cases, due to damage to the muscle layer of the bladder, urinary incontinence occurs.
Cystitis can become a manifestation of any urological disease, so the clinical picture largely depends on the nature of the underlying pathology. In addition, the symptoms of the disease may include signs of inflammatory diseases of the organs of the reproductive system. Unfortunately, this combination is extremely common in women.
Causes of cystitis
The pathology is one of the polyetiological ones (that is, multiple causes), so several factors contribute to its development. The main cause is the entry of various microorganisms into the bladder. In almost 90% of cases, it is E. coli, which lives in the rectum and is located near the urinary organs. Also, the inflammatory process is caused by other bacteria and microorganisms: Candida fungi, chlamydia, herpes virus, etc.
Pathological organisms can enter the urinary system in different ways. There are the following penetration methods:
- Ascending. Most often, pathogenic microflora enters the bladder through the urethra.
- descending. In this case, microorganisms penetrate from the kidneys (for example, in the presence of pyelonephritis).
- Lymphogenic. Associated with the flow of lymph, through which organisms enter the bladder from other organs of the small pelvis, in the presence of inflammation in them.
- Hematogenous. Infection occurs from distant foci of inflammation due to blood flow.
There are several reasons why cystitis is more common in women than in men. This includes the following:
- A special structure of the reproductive system, which contributes to the spread of bacteria and infections in the urinary system.
- A short urethra, located near the anus (a place where various bacteria accumulate).
- Frequent hormonal fluctuations, which can weaken the body's immunity.
Risk factors
There are factors that increase the risk of developing bladder inflammation. This includes:
- Hypothermia of pelvic organs.
- Reduced immunity.
- Constant overload, frequent stress.
- Violation of intimate hygiene rules.
- A penchant for prison.
- Abuse of spicy and spicy food.
- Stagnation in the pelvic organs.
- Chronic pathologies of the genitourinary system.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Congenital pathologies of urinary organs.
Another factor for the development of such an infection is pregnancy. According to statistics, every 10th pregnant woman experiences symptoms of cystitis. This condition leads to a decrease in general immunity, changes in hormonal levels, an increase in the size of the uterus and a deterioration in the blood supply to the bladder.
Also, the disease is often diagnosed in menopausal patients. At the age of 50-55, estrogen levels decline, which often leads to a weakening of the bladder lining.
In many patients, acute or chronic cystitis manifests itself during menstruation. This is because bacteria enter the urethra along with menstrual blood. The following factors can cause such a condition during menstruation:
- Thrush or other infectious pathologies.
- Inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs.
- Decreased general immunity.
- Sexually transmitted infections.
- Allergic reaction to pads or tampons.
- Non-observance of hygiene rules.
Features of treatment
The diagnosis of "cystitis" is made based on the patient's complaints and an examination by a urologist or gynecologist, and some tests and instrumental examinations are also required.
The doctor prescribes the woman:
- general urinalysis;
- clinical blood test;
- urine culture, bacteriological examination (if complicated cystitis is suspected).
In the case of a recurrent course of the disease, swabbing and seeding of vaginal discharge, analysis of antibodies to the herpes virus, scraping from the urethra and cervical canal may be prescribed. These procedures help identify factors that cause relapses.
Instrumental techniques are also important in the diagnosis of pathology. Among them:
- Ultrasound of pelvic organs and bladder.
- MRI of the genitourinary system.
- Cystoscopy with biopsy (with complicated or recurrent course).
Such diagnostic procedures allow you to determine the presence of pathology and the causes of its occurrence. Based on the data obtained, the specialist can create a treatment regimen for cystitis. Therapy is based on an integrated approach, which aims to achieve the following goals:
- Implementation of antibacterial and symptomatic therapy, elimination of existing symptoms.
- Prevention of possible complications.
- Prevention of recurrence of pathology.
Antibacterial and symptomatic therapy includes taking various drugs. These can be painkillers, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory drugs, antispasmodics, etc. The purpose of their application is to relieve symptoms and eliminate the existing inflammatory process. In addition, the doctor can prescribe immunomodulators or multivitamin complexes. If cystitis recurs, bacteriophage-based preparations are often used.
In addition, it is possible to prescribe various physiotherapeutic methods. Among them:
- Electrophoresis. It helps relieve inflammation and relieves cramps.
- Magnetotherapy. It eliminates bacteria and viruses in the inflamed organ.
- Inductotherapy. Contributes to the normalization of blood flow, normalizes the urinary system.
Also, the patient is recommended to follow several rules:
- Exclude spicy, spicy and salty foods, carbonated drinks, coffee, alcohol and sweets from your diet.
- Refrain from sexual intercourse during treatment.
- Drink plenty of water (acidic fruit drinks and urology allowances are also recommended).
- Avoid physical activity (including swimming in pools and ponds).
Important!Traditional medicine methods have no proven effectiveness, so they can only be used in combination with medicines. You cannot use folk remedies on your own - be sure to consult your doctor!
Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis, with some exceptions. Hospitalization of the patient is sometimes required, and the indications for this may be:
- Severe course of the disease.
- The presence of serious concomitant diseases (for example, diabetes mellitus).
- Occurrence of complications.
- Decompensated heart failure.
- Ineffectiveness of current antibiotic therapy.
Symptoms and treatment of acute cystitis
The acute form develops quickly against the background of the relative health of the patient. The main symptom is frequent urination. Symptoms such as severe pain, burning during urination, symptoms of intoxication and elevated temperature are also characteristic of acute cystitis in women.
There is a rapid increase in symptoms and an increase in the number of urination during the first day. Intervals between urination can be reduced to 5-15 minutes. At the same time, urges occur both during the day and at night.
The condition can be accompanied by the appearance of blood in the urine and purulent discharge. The acute form of the pathology lasts on average up to 7-10 days, without the lack of appropriate treatment, the disease becomes chronic with stages of deterioration.
Symptoms and treatment of chronic cystitis
This phase develops as a result of improper and/or untimely treatment of the inflammatory process. Often, the pathology is the result of self-medication and uncontrolled drug intake.
In addition, the chronic form can be a consequence of other diseases of the genitourinary system. Cystitis is often diagnosed in patients with pyelonephritis, vulvovaginitis and various infections of the reproductive and urinary systems.
The danger of chronic cystitis is that it occurs without pronounced symptoms. A woman may experience exacerbations followed by remission, during which there are no problems with urination. However, during exacerbations, symptoms similar to the acute form appear. There is frequent urination with pain and pain, blood or purulent discharge often appears in the urine.
In the treatment of chronic cystitis, it is important to eliminate the factors that constantly cause relapses. For example, during menopause and in the presence of hormonal disorders, hormone replacement therapy is prescribed. In some cases, surgery may be required to correct congenital defects in the urinary system.
Possible complications
The key to successful treatment of cystitis is a timely visit to the doctor. As a rule, in such cases, therapy does not last longer than 10-12 days. However, in the absence of medical care and failure to follow the doctor's recommendations, the patient may experience a chronic form of the disease. In this case, complications are not excluded, including:
- pyelonephritis;
- paracystitis;
- abscess;
- urinary incontinence;
- violation of the reproductive function of the body.
Preventive therapy is recommended for patients with frequently recurring cystitis (more than 3 exacerbations per year) to prevent possible complications. It involves taking small doses of antibiotics, but such treatment is carried out only according to the doctor's instructions.
Disease prevention
In most cases, simple preventive measures help to avoid the development of cystitis. Including, you need:
- Proper hygiene of external genital organs.
- Observe hygiene during sexual activity.
- Drink enough clean water daily.
- Eliminate all provoking factors (stress, hypothermia, a large amount of spicy and spicy food).
- Seek medical help in time and do not treat diseases of the pelvic organs yourself.
It is also important to remember that during cystitis it is forbidden to visit a bath / sauna or to overheat the body in any way (including using a heating pad in the lower abdomen). In the presence of a bacterial form of the disease, the reproduction of pathogenic microflora can be triggered. And that increases the risk of developing an abscess. If the disease is of a different nature, then heating the tissue will accelerate blood microcirculation. This can cause blood to enter the urine and increase the pain.
In the prevention of cystitis, regular emptying of the bladder and intestines is important. Also, a woman is recommended to lead an active lifestyle, include physical activity in the daily routine. This will eliminate congestion in the pelvic organs and normalize the urination process.
Cystitis is an extremely unpleasant disease, because it has a rapid course and can affect the quality of life. However, a correct and rational approach to treatment allows you to quickly eliminate all symptoms of the disease and avoid various complications. The most important thing in this case is not to self-medicate and not to delay contacting a doctor.
Important!
The information in this article should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. You should always consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.